Understanding Common Obsessions and Interests in Autism
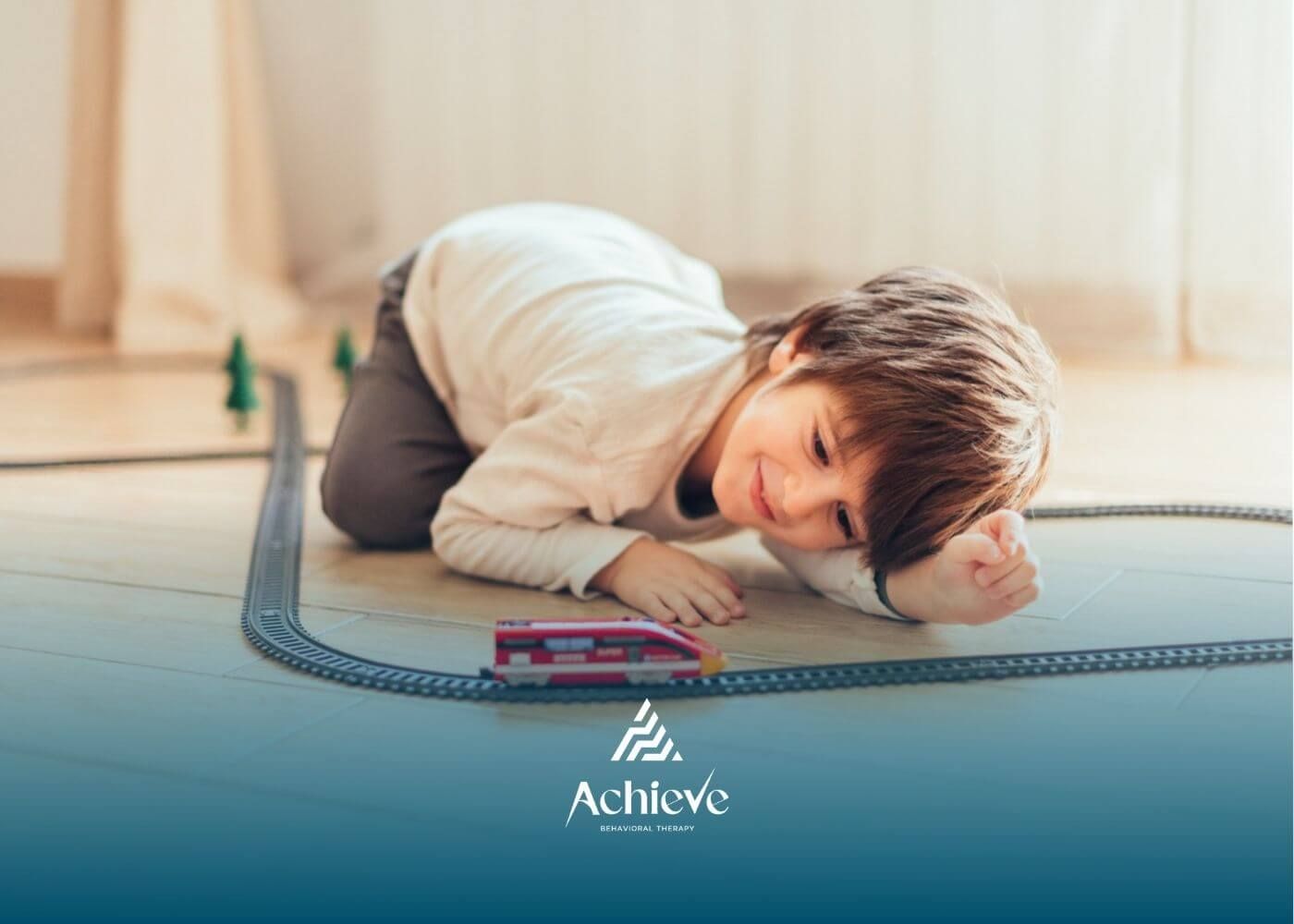

Obsessions (often called special interests) are very common in autism. They involve deep, focused attention on certain topics, objects, routines, or sensations. These interests can be comforting, motivating, and even a strength.
Understanding them helps families support their child in a positive, respectful way.
Special interests in autism
Autistic individuals often develop intense interests that bring joy and a sense of control. While every child is unique, some patterns show up more often than others.
Objects and collections
Some children become very focused on specific objects or categories of items, such as:
- Trains, cars, buses, or airplanes
- Dinosaurs, animals, or insects
- Toys with moving parts
- Household items like fans, doors, elevators, or wheels
- Collecting rocks, buttons, or small figures
Topics and facts
Many autistic children enjoy learning everything about one subject and sharing that knowledge repeatedly.
Common topic-based obsessions include:
- Space, planets, rockets, or weather systems
- Geography, maps, flags, or countries
- History, timelines, or famous events
- Specific TV shows, movies, or video game characters
- Science topics like volcanoes or the human body
Letters, numbers, and symbols
A strong interest in symbols and systems is also common, especially in younger children.
This may look like:
- Letters and phonics
- Numbers, counting, or math facts
- License plates or street signs
- Calendars, dates, and schedules
- Clocks and telling time
Patterns, order, and organization
Many autistic individuals enjoy predictability and structure.
This can include:
- Lining up toys or objects
- Sorting by color, size, or type
- Creating detailed lists
- Organizing items in very specific ways
- Repeating the same actions in the same order
Routines and sameness
A strong preference for routine often shows up as:
- Wanting the same daily schedule
- Eating the same foods
- Wearing the same clothing styles
- Taking the same route to familiar places
- Becoming upset when plans change
Sensory-focused interests
Some obsessions are tied to sensory experiences that feel calming or regulating.
Examples include:
- Watching spinning or rotating objects
- Repeating sounds, songs, or phrases
- Touching certain textures repeatedly
- Focusing on lights, shadows, or reflections
- Smelling or tasting specific items
Technology and mechanics
Older children may show strong interests in how things work.
This can include:
- Computers, tablets, or coding
- Video games and game systems
- Mechanical parts and tools
- Building systems like LEGO or circuits
When obsessions may need support
Special interests are not a problem on their own. Support may be helpful if they:
- Take over most of the day
- Cause distress when interrupted
- Interfere with learning or social interaction
- Make transitions extremely difficult
The goal is balance — not removing what a child loves.
How ABA therapy can support healthy balance
Ethical, modern ABA therapy uses a child’s interests as motivation for learning rather than trying to eliminate them. Therapists help children build flexibility, communication, and coping skills while respecting their passions.
At Achieve ABA, therapy is personalized and child-centered. Our team works with families to support growth in ways that feel positive and meaningful.
We offer:
- In-home ABA therapy for learning in a comfortable setting
- School-based ABA to support success in the classroom
- Telehealth ABA for flexible access to care
- Early intervention for autism for young children
Families in New Jersey and North Carolina can access these services locally.
Want support that respects your child’s interests while building real-world skills? Reach out to Achieve ABA to learn how personalized therapy can help your child thrive.
FAQs
Are obsessions always a negative thing in autism?
No. Many special interests bring joy, reduce anxiety, and support learning when guided appropriately.
Should parents limit special interests?
Limits can help with balance, but interests should be respected and used as motivation rather than taken away.
Do special interests change over time?
Yes. Some last for years, while others shift as children grow and discover new interests.
Sources:
- https://www.autism.org.uk/advice-and-guidance/topics/about-autism/preference-for-order-predictability-or-routine
- https://www.autism.org.uk/advice-and-guidance/topics/about-autism/focused-and-dedicated-interests
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4543385/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2676040/
- https://www.kennedykrieger.org/stories/interactive-autism-network-ian/challenging_behavior_restricted_interests
Need Support?
We're Here to Help!
Our experienced team is ready to assist you. Reach out today to discuss how we can support your child's development and well-being.
Get started with expert ABA therapy today.